In the fifth year of the North Carolina Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC)’s “Keep Our Air Clean” Student Art Contest, students in North Carolina from kindergarten through high school submitted their artwork for a chance to be featured on billboards across the state. Students were asked to create art focused on actions that people can take to reduce air pollution from vehicles and help keep the air clean. NCCETC congratulated three artists located in Morrisville, Weddington and Raleigh, N.C.
The art contest originated from Heather Brutz, Interim Director of the Clean Transportation Program at NCCETC, who thought of the Student Art Contest while recalling her previous experience as a middle school teacher. “I hoped the contest could engage young people’s creativity to help spread awareness about the ways we can reduce air pollution from vehicles,” Brutz said.
Air pollution is one of the ways climate change impacts our health today, with the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS) reporting almost 9 out of 10 people who live in urban areas worldwide are affected by air pollution. The NIEHS explains air pollution can affect lung development and increase the amount and seriousness of lung disease and asthma. Children, the elderly, and people living in areas with high levels of air pollution are especially susceptible.
“Clean air is vital for health,” Brutz said. “This is true for people of all ages, but there is research that shows that exposure to air pollution for kids increases their chances of getting asthma, which affects their health for the rest of their lives.”
As a teacher, Brutz would try a variety of different teaching methods to capture students’ attention. “I applied that same thinking when I first came up with the idea for the art contest- I wanted to engage a different audience than we sometimes interact with in our other educational activities at the Center and engage that audience in a different way than what we were already doing,” explained Brutz. “Artwork is a powerful tool and I was excited to find a way to work together with young artists to help spread the message about ways we can keep our air clean.”
NCCETC received submissions from students in elementary, middle and high schools across the state. “It’s always rewarding to see how creative students are with their work,” said Brutz. “Although we are only able to choose three winners whose artwork will be displayed on billboards, every single young artist who submitted should feel proud of their contribution.”
To learn what clean air means to them, we asked the winners some questions about their artwork:

Elementary School Winner – Sudeep Asam | Morrisville Elementary School | Morrisville, NC
Why did you want to enter the contest?
I want to express my feelings in the “keep our air clean” contest.
What does your artwork mean/what were you trying to express?
My artwork expresses how pollution spoils our environment and ways to stop the pollution and be a solution.
What does “keep our air clean” mean to you? Why do you think keeping our air clean is important?
If our air is clean, people and nature stay healthy.
Are you doing things in your own life – like riding your bike, carpooling, walking, etc?
Yes, I do walking and biking.
What was your reaction when you found out you won the contest?
I feel very happy.
What do you hope will come out of your artwork being up on a billboard for people to see?
I am hoping my artwork inspires some of the people and will start working on stopping pollution.
Anything else you’d like to share.
Everyone should take a pledge to stop the pollution and be a solution.

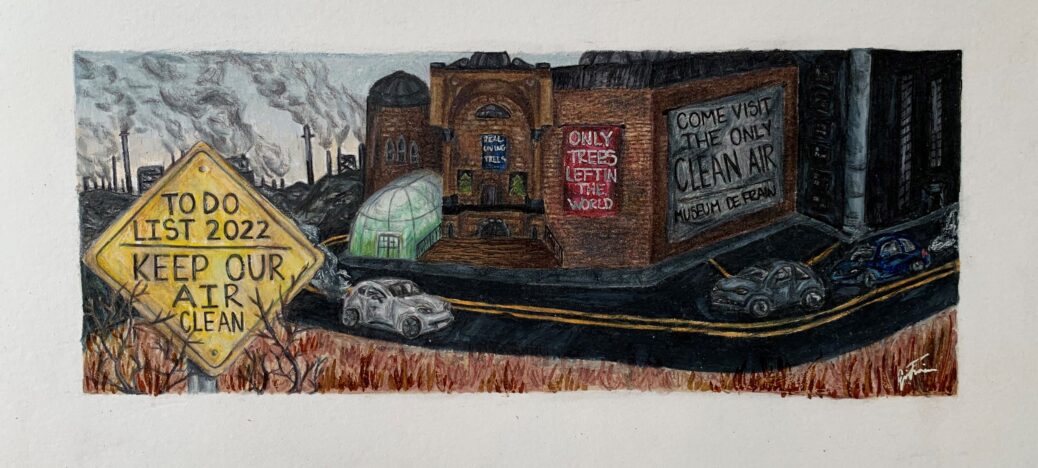
Middle School Winner – Evie Frain | Weddington Middle School | Weddington, NC
Why did you want to enter the contest?
I entered this contest with the purpose to show the progression of pollution, because it is commonly seen as something intangible. People often think that climate change, pollution, and global warming are far off in the future, when in reality they aren’t.
What does your artwork mean/what were you trying to express?
My artwork is meant to express that the current rate of fossil fuel burning is dangerous to both the lives of humans and the environment.
What does “keep our air clean” mean to you? Why do you think keeping our air clean is important?
To me, “keep our air clean” stresses the importance of conscientious efforts today. Clean air is needed for all living organisms, so the viability of the future depends on us acting now.
Are you doing things in your own life – like riding your bike, carpooling, walking, etc?
I try to carpool and limit the amount of places I have to go.
What was your reaction when you found out you won the contest?
I was surprised, I had never expected to win. I only put my artwork into the contest because I am passionate about switching to clean energy.
What do you hope will come out of your artwork being up on a billboard for people to see?
I hope people will rethink some of their own personal uses of fossil fuels and find a way to limit them.
Anything else you’d like to share.
Besides limiting fossil fuels, it’s also environmentally beneficial to recycle and reuse items.

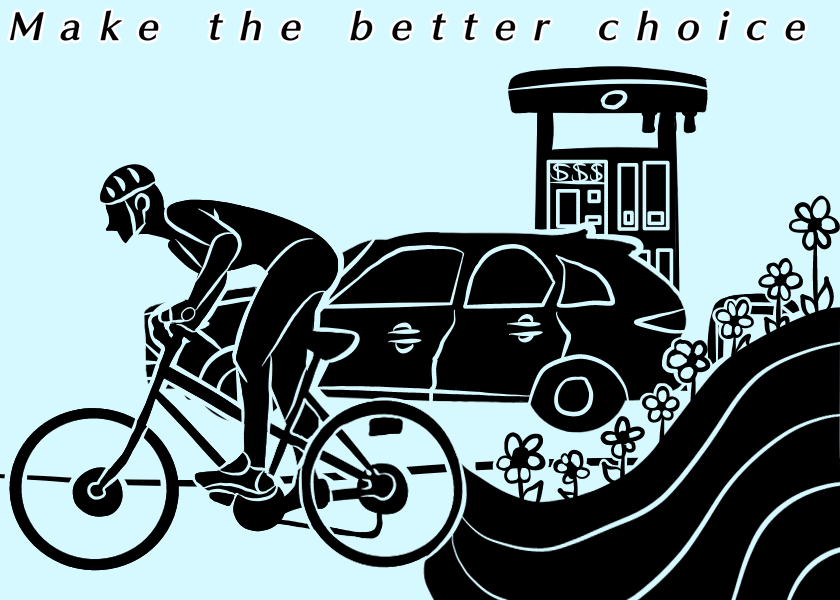
High School Winner – Emilyn Haddock | Broughton High School | Raleigh, NC
Why did you want to enter the contest?
The reason why I wanted to enter the contest was to get the chance to express my artwork. There are rare times in my life I was able to have a chance to submit my artwork into a contest. Usually when I enter my creations, I do it for the sole purpose of expressing my work and have a chance for someone to review. It is nice to see my artwork being appreciated and to be seen by people.
What does your artwork mean/what were you trying to express?
My meaning behind my artwork is to have a conscious decision between riding your bike to work or to your local grocery store then potentially spending more money on gas and burn more carbon fuel.
What does “keep our air clean” mean to you? Why do you think keeping our air clean is important?
The phrase “keep our air clean” means that keeping toxic fumes in our air we breathe. We take clean air for granted and if we don’t appreciate and take measures of keeping it clean, masks will be more ingrained to our daily routine then the pandemic. It is important to keep our air clean because having unclean air can cause health problems, terrible living conditions and people with breathing conditions will have a much harder time going outside. Keeping our air clean also means some caring about other peoples health by going to measures of reducing carbon fuel and debris in the air.
Are you doing things in your own life – like riding your bike, carpooling, walking, etc?
Yes! I have bought my own bicycle so that I can easily travel to my local stores. Recently, I have the responsibility of buying grocery items for my parents to make dinner so having a bike makes it 10 times more faster to get to my destination and 10 times more fun.
What was your reaction when you found out you won the contest?
It was actually two months after I found out that I won the contest. I wish I found out sooner because I was traveling with my parents over the summer outside of America, so my phone was practically dead. Having to find out now is pretty exciting and gave me butterflies in my stomach.
What do you hope will come out of your artwork being up on a billboard for people to see?
I hope that the next time they drive by my billboard, they would’ve use their bikes or scooters instead for the next time they wanna go out. Riding your bike is a totally different experience than just driving your car.
Anything else you’d like to share.
The last thing I wanted to share is, I hope my local government makes more sidewalks or bike lanes for bikers like me that can travel more openly and safer for me to travel. As much as I want to make a good decision on riding my bike instead of driving, I cannot take full advantage of riding my bike to father destinations if there is no extended sidewalks for me to go. If they’re more sidewalks, I my prediction will be that more people will be willing to walk or use their scooters then traveling with cars.
What was your reaction when you found out you won the contest?
It was actually two months after I found out that I won the contest. I wish I found out sooner because I was traveling with my parents over the summer outside of America, so my phone was practically dead. Having to find out now is pretty exciting and gave me butterflies in my stomach.
Anything else you’d like to share.
The last thing I wanted to share is, I hope my local government makes more sidewalks or bike lanes for bikers like me that can travel more openly and safer for me to travel. As much as I want to make a good decision on riding my bike instead of driving, I cannot take full advantage of riding my bike to father destinations if there is no extended sidewalks for me to go. If they’re more sidewalks, I my prediction will be that more people will be willing to walk or use their scooters then traveling with cars.
Thank you to all you participated in the 2022 Student Art Contest!
![]()