The burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market is leading the way towards an emissions-free future, but the growing electrical demand on the nationa’s grid needed to fuel EVs risks further complicating utilities’ careful balancing act to integrate an expanding supply of variable renewables.
The NC Clean Energy Technology Center (NCCETC) at NC State University recently hosted a webinar session to highlight innovations in managed charging and recent EV policy trends in the United States. With legislation and technology advancements accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the United States, utilities and fleet technology companies are learning how to respond to the increasing charging demand on the nation’s electrical grid.
The webinar titled 50 States of Electric Vehicles and Innovations in Managed Charging was part of the NCCETC’s Energy & Sustainability Services Webinar Series. NCCETC’s Senior Clean Transportation Specialist Lisa Poger moderated the panel discussion with Brian Lips of NCCETC, Elaine Jordan of Duke Energy and Jacqueline Piero of The Mobility House.
POLICY PAVING THE WAY FOR ELECTRIC VEHICLES
The session began with an overview of EV policies in the 50 States from Lips featuring information from the Q1 2022 and Q2 2022 editions of The 50 States of Electric Vehicles. “In the first half of the year, every single state took some sort of policy action related to EVs,” Lips said. “It’s a very popular topic among policymakers.”
Lips serves as manager of the Database of State Incentives for Renewables and Efficiency (DSIRE) project, a publicly available resource on federal, state and utility policies and incentives for renewable energy, efficiency, energy storage, and electric vehicles operated by the Energy Policy Team at NCCETC. Additionally, DSIRE Insight expands upon DSIRE with the 50 States quarterly reports and subscription services focused on distributed solar, grid modernization and energy storage, and electric vehicles, as well as customized energy policy research.
“In both quarters, we saw the most activity in the financial incentives category,” said Lips. Financial incentives include bills related to tax credits or other incentive programs.
For the first half of 2022, the DSIRE Insight team has observed six trends in EV-related policy actions taken: (1) states encouraging zero-emissions school bus deployment, (2) utilities proposing charging-as-a-service programs, (3) states and utilities continue examining demand charge alternatives for commercial charging, (4) states planning for federal EV infrastructure funding, (5) state lawmakers addressing charging infrastructure siting issues, and (6) utilities developing active managed charging pilot programs.
“We’re seeing a lot of states encouraging or requiring the deployment of zero emission school buses,” stated Lips. Legislation enacted in New York during the second quarter of 2022 requires that all school buses in the state be zero-emission by July 2035, as noted by The 50 States of Electric Vehicles: Q2 2022 Quarterly Report Executive Summary.
INNOVATIONS IN MANAGED CHARGING & PILOT PROGRAMS
With no other market interventions, EV owners who commute to work could be inclined to charge their vehicles when they return in the late afternoon and exacerbate these growing demand curves. However, with proper incentives or more direct utility involvement to shift the EV demand curve, EV charging could provide a myriad of benefits to consumers and the electric system as a whole.
While the EV industry and its effects on the grid are still very new and vary from state to state, utilities have started exploring different approaches to influence customer charging behavior, commonly referred to as managed charging. DSIRE Insight’s blog Recent Developments in Managed Charging explains the distinction between active and passive managed charging: Passive managed charging uses price signals like time-varying rates or peak time rebates to encourage customer behavior, while active managed charging gives utilities direct control over the load similar to a demand response program
A growing number of utilities are filing applications to offer charging-as-a-service programs or developing managed charging pilot programs to minimize grid impacts and provide system-wide benefits. “Entergy requested approval for new offerings like this in Arkansas and Mississippi,” Lips said. “While DTE Electric in Michigan proposed residential and commercial charging-as-a-service programs this year and Indiana regulators approved another program proposed by Duke Energy.”
Elaine Jordan, Senior Rates and Regulatory Analyst, provided a brief overview of the two managed charging pilot programs under development by Duke Energy in their North Carolina jurisdiction.
“We’re really excited because we’ve had the opportunity to partner with BMW, Ford and General Motors,” Jordan said. One of the pilot programs will test the new Open Vehicle Grid Integration Platform, a telematics based platform that enables Duke Energy to receive charging data from customers with exact kilowatts consumed for each charging session.
The second pilot program is a Demand Response Pilot utilizing vehicle-to-grid technology which allows Duke Energy to discharge EV batteries to support the grid. Duke Energy’s proposal for this pilot is still under consideration by the North Carolina Utilities Commission.
SMART CHARGING FOR SMART SAVINGS
Organizations like The Mobility House are working with fleets and customers to create smart charging solutions and strategies that not only lower costs and deliver savings, but also use EV batteries as a beneficial part of the power grid. Jacqueline Piero is the Head of Policy and Regulation in the United States for The Mobility House.
“If you have demand charges, we’ll also make sure that we’re minimizing the impact charging EVs will actually have on that demand- which can be the biggest part of an electric bill,” said Piero. “The last thing we want to do is have electric vehicles be more expensive than having diesel or gas vehicles.”
While utilities are beginning to adapt to manage EV charging, private companies such as The Mobility House are able to offer charging solutions to enable fleets to electrify at the least cost possible in the current environment. With The Mobility House’s load control technology, King County Metro in Washington state has been able to put more EVs and charging stations behind the meter than the grid connection should be able to allow.
“We have 4.63 megawatts of transit bus charging happening behind a 2.5 megawatt connection, and we’re doing that by having on-site control,” Piero said. In total, King County Metro saved around $1 million by using the existing grid connection and saves an additional $100,000 a year in operating expenses.
Piero hopes flexible approaches like the King County pilot program can be a model to further propel the transition to electric buses throughout the country. With collaboration from utilities, automotive manufacturers and third parties like The Mobility House, customers can feel more at ease with making the switch to an EV and the grid will stay up and running when they do.
ABOUT THE DATABASE OF STATE INCENTIVES FOR RENEWABLES AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY:
DSIRE is the most comprehensive source of information on incentives and policies that support renewable energy and energy efficiency in the United States. Established in 1995, DSIRE is operated by the NC Clean Energy Technology center at NC State University. If you’re interested in learning more about incentives and policies for renewable energy and energy efficiency in your state, visit DSIREusa.org.
ABOUT NCCETC’S ENERGY & SUSTAINABILITY SERVICES:
The NCCETC is now offering Energy & Sustainability Services (ESS) to all types of private and public organizations. Our staff are subject experts in clean energy, transportation, policy and workforce development and they bring this entire portfolio of knowledge toward a holistic approach to client work. They also provide unbiased, data-driven, and technical fee-for-service energy solutions based upon the client’s specific needs.
Register for our newsletter to stay tuned for the next free webinar highlighting timely topics and services!

 The State of the Green Mobility Industry in the Southeast: Market Trends and Policies Driving Transportation Electrification
The State of the Green Mobility Industry in the Southeast: Market Trends and Policies Driving Transportation Electrification Florida, Georgia, North Carolina and South Carolina have become leaders in the deployment of EV charging infrastructure in the Southeast. Furthermore, Tennessee is showing great strength for fast charging deployment specifically, with the Department of Environment and Conservation working in partnership with the Tennessee Valley Authority to develop a statewide EV fast charging network.
Florida, Georgia, North Carolina and South Carolina have become leaders in the deployment of EV charging infrastructure in the Southeast. Furthermore, Tennessee is showing great strength for fast charging deployment specifically, with the Department of Environment and Conservation working in partnership with the Tennessee Valley Authority to develop a statewide EV fast charging network.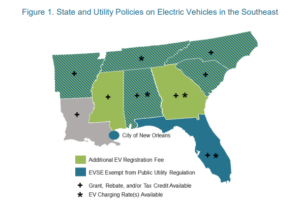 The Policy & Markets team at NCCETC maintains the
The Policy & Markets team at NCCETC maintains the 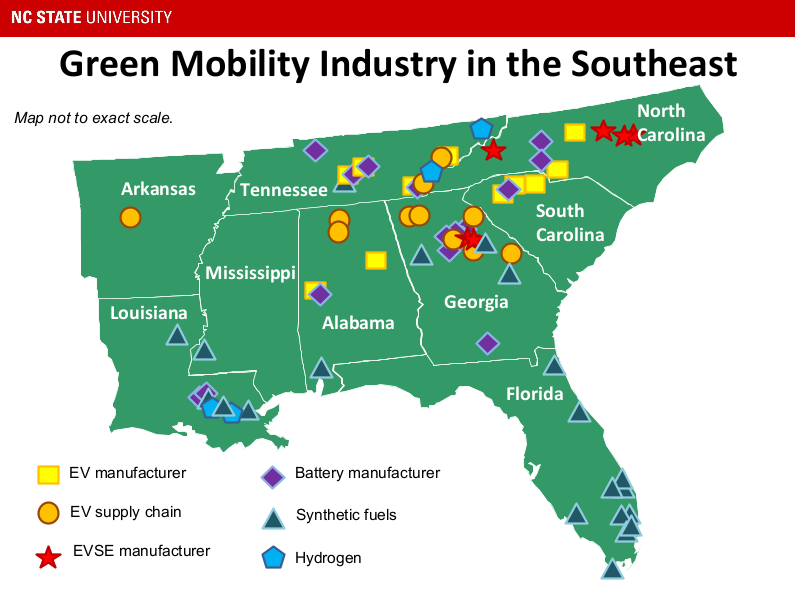 For interested Dutch investors, the southeastern states with the greatest opportunity depend on which aspects of the green mobility industry best fit the interests of Dutch companies, according to the report. One of the largest cross-cutting trends for the region is the importance of the automotive industry. “Most of the states in the Southeast are home to either vehicle assembly plants or automotive supply chain manufacturers,” said Heather Brutz, one of the report’s authors and Finance & Operations Manager for NCCETC’s Clean Transportation program.
For interested Dutch investors, the southeastern states with the greatest opportunity depend on which aspects of the green mobility industry best fit the interests of Dutch companies, according to the report. One of the largest cross-cutting trends for the region is the importance of the automotive industry. “Most of the states in the Southeast are home to either vehicle assembly plants or automotive supply chain manufacturers,” said Heather Brutz, one of the report’s authors and Finance & Operations Manager for NCCETC’s Clean Transportation program.

